.png)
The declining use of cash, which has already taken a substantial hit over the past decade, is accelerating due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Both the fears of contracting COVID-19 through cash and the steep reduction of in-person purchases amid lockdowns have accounted for a significant decline in cash transactions during 2020.
McKinsey & Company, a global management consulting firm, reported in their 2020 Global Payments Report that an estimated 28 percent of total transactions in the U.S. were executed via cash in 2020 —down from 51 percent in 2010.
TSYS, a payments technology company, found that 80 percent of consumers indicated either a debit or credit card as their preferred payment type, according to the 2018 TSYS U.S. Consumer Payment Study. Only 14 percent of consumers indicated cash as their top choice when paying for an item. The rapidly growing e-commerce market has led to further reductions in cash usage. While retail sales are expected to decrease in 2020, e-commerce sales are expected to grow to what will be a record-shattering 31.8 percent increase in revenue. 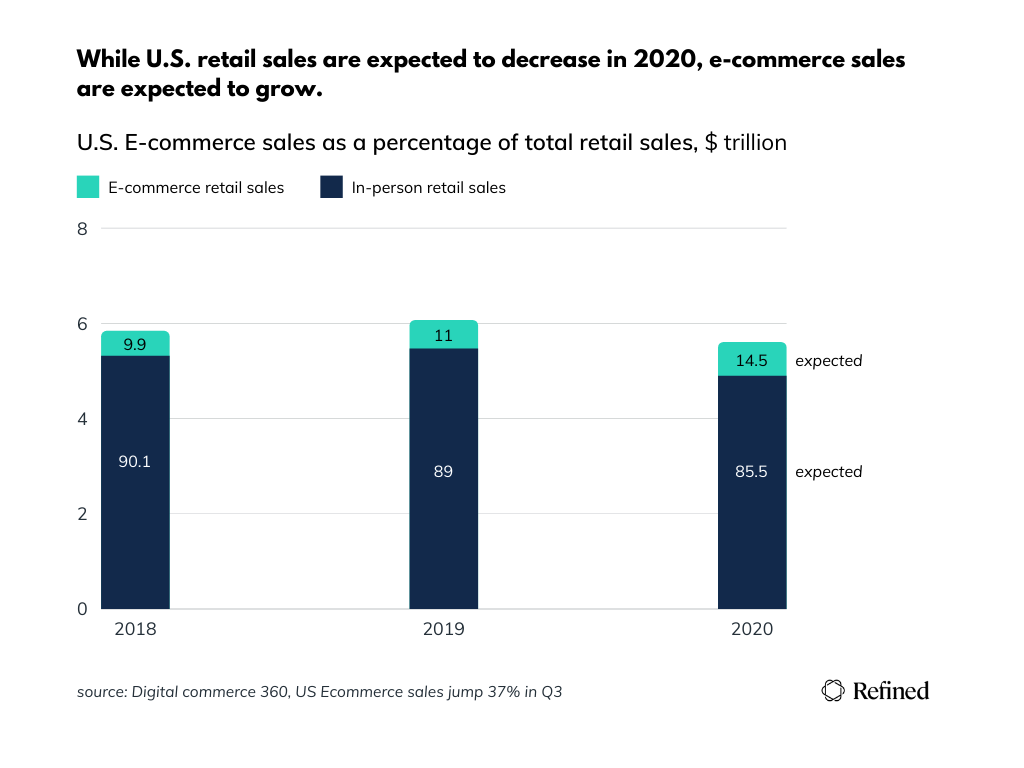 The rise of digital wallets and mobile payment apps are also major factors driving the trend towards cashless commerce. According to TSYS in 2018, 23 percent of those surveyed indicated they made an in-store purchase using a merchant’s mobile app, which connected to a debit or credit card. TSYS also found that 82 percent of consumers aged 18-24 were familiar with in-app purchases, compared to 41 percent of consumers aged 65 years or older. The growing digital wallet and mobile payment app usage is expected to compound the cashless trend in the next five to ten years.
The rise of digital wallets and mobile payment apps are also major factors driving the trend towards cashless commerce. According to TSYS in 2018, 23 percent of those surveyed indicated they made an in-store purchase using a merchant’s mobile app, which connected to a debit or credit card. TSYS also found that 82 percent of consumers aged 18-24 were familiar with in-app purchases, compared to 41 percent of consumers aged 65 years or older. The growing digital wallet and mobile payment app usage is expected to compound the cashless trend in the next five to ten years.
Embracing cashless
Many businesses have recently embraced going digital to increase efficiency and customer satisfaction by offering contactless payments, adopting online ordering systems and building mobile apps for their customers, as a result of the reductions in cash usage. A small percentage of businesses have resisted digital commerce in an attempt to avoid the fees typically associated with digital payments. However, can the avoidance of digital commerce negatively affect their bottom line? To answer this question, we looked at the hidden cost of only accepting cash.
The most significant hidden cost of cash for businesses is the potential loss of sales due to not accepting digital payments. According to CNBC, “By not accepting cards, those 15 million businesses are missing out on $100 billion in sales annually—roughly $7,000 per company a year in either new sales or sales that go to competitors.” Due to the loss of ATM revenue, many banks are now charging on the deposit side, particularly for business accounts. Both Wells Fargo and Bank of America charge business customers 30 cents per $100 deposited. For a business depositing $500,000 per year, this cost can equate to $1,500 per year. This doesn’t factor in the additional cost of cash handling, or the time required to manage cash, including counting, driving and depositing.
Tools for digital commerce
Similar to the invention of the drive thru, online ordering systems and mobile apps were designed to minimize pain points and increase customer convenience. Both of these technologies allow businesses to accept orders and payments from customers online—through a website or an app, which can effectively reduce labor costs and increase efficiency. The adoption of these technologies can lead to greater productivity and profitability across an organization. As online orders increase, phone orders may decrease, freeing up time for employees to focus on other duties.
Recommendations
We forecast the use of cash in its physical form will continue to decline as lockdowns are lifted. Both the Covid-19 pandemic and the emergence of peer-to-peer apps, such as Cash App and Venmo, will likely lead to a further decline in cash usage. The shifts toward e-commerce and digital payments (including contactless) as well as the rise of merchant mobile apps will also likely continue to be primary factors in this decline. Businesses should be adaptive to digital commerce and utilize the technology for accepting contactless payments, online ordering systems and mobile apps to address customer’s needs and remain relevant in the current environment and the post-pandemic future.